Grow Tips - HEIR GENETICS
Understanding Plant Anatomy
Knowing the anatomy of the plant is key to maximizing growth and yield. Each part of the plant plays a role in photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and development.
Roots
The root system anchors the plant and absorbs water and essential nutrients. Strong, healthy roots are fundamental to successful growth.

Stem
The stem transports nutrients and water throughout the plant. It also provides structural support, allowing leaves to reach the light.

Leaves
Leaves are the main site for photosynthesis, where sunlight is converted into energy. They also help regulate water loss through small openings called stomata.

Flowers
The flowers are the plant’s reproductive organs and are crucial for producing seeds and, ultimately, the harvest.

Plant Physiology
Plants convert light into energy through photosynthesis, a process that occurs mainly in the leaves. Water and nutrients are taken up through the roots and transported to the leaves, where chlorophyll pigments absorb light and produce energy.
Key processes like nutrient uptake, transpiration, and photosynthesis all contribute to growth. Understanding these processes can help you optimize conditions for plant health and productivity.

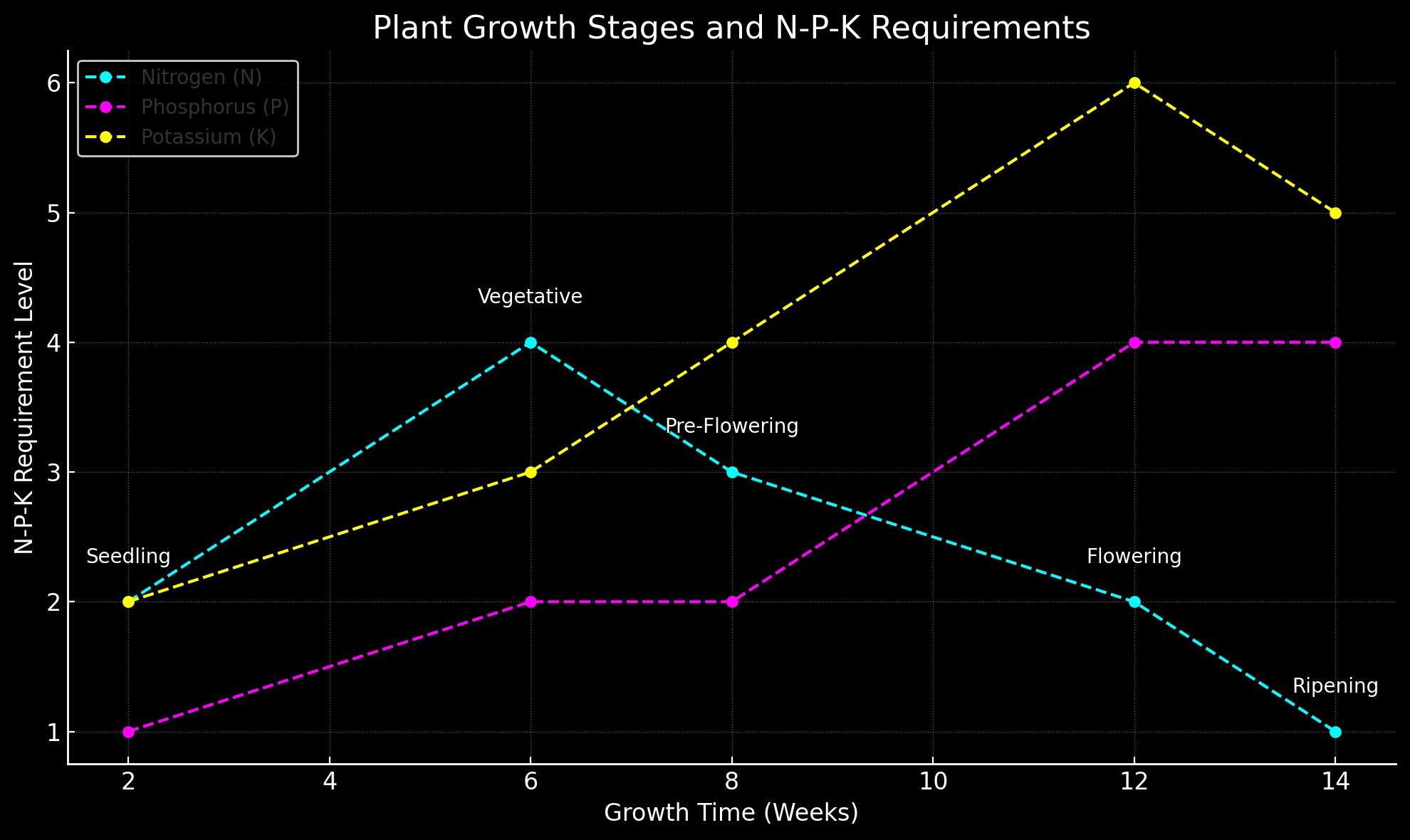
Nutrient Basics (N-P-K) & Fertigation Techniques
N-P-K Ratios
The three primary nutrients plants need are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Here’s a basic breakdown of their roles:
- Nitrogen (N): Promotes leaf growth and overall plant vigor.
- Phosphorus (P): Supports root development and flower/bud formation.
- Potassium (K): Essential for overall health, improves disease resistance and stress tolerance.

Fertigation Techniques
Fertigation is a method of delivering nutrients through irrigation, allowing for precise control over the amount and timing of nutrient delivery. Here are some popular fertigation techniques:
- Drip Irrigation: Minimizes water and nutrient waste by delivering them directly to the roots.
- Flood and Drain: Nutrient solution floods the grow area and is then drained away, effective for hydroponic systems.
- Foliar Feeding: Nutrients are sprayed onto leaves for direct absorption, ideal for quick nutrient uptake during specific growth phases.
Grow Mediums
Choosing the right grow medium is essential, as it affects water retention, root aeration, and nutrient availability. Here’s an overview of three common mediums:
Soil
Soil is a natural medium that provides nutrients and stability. It’s ideal for beginners due to its forgiving nature.
- Pros: Holds nutrients well, easy for beginners, provides natural microbial life.
- Cons: Slower growth compared to other mediums, risk of pests, pH needs frequent monitoring.

Coco Coir
Made from coconut husks, coco coir is a sustainable, lightweight, and pH-neutral option.
- Pros: Good aeration, better water retention than soil, eco-friendly.
- Cons: Requires specific nutrients, must be kept moist, can attract mold if not maintained.

Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a soil-less system where plants grow in a nutrient-rich solution, promoting faster growth and higher yields.
- Pros: Rapid growth, efficient nutrient use, no soil pests.
- Cons: Requires careful monitoring, high initial cost, potential for root diseases in unclean water.

Growth Chart
Insert a graph here to show growth stages and N-P-K requirements over time.